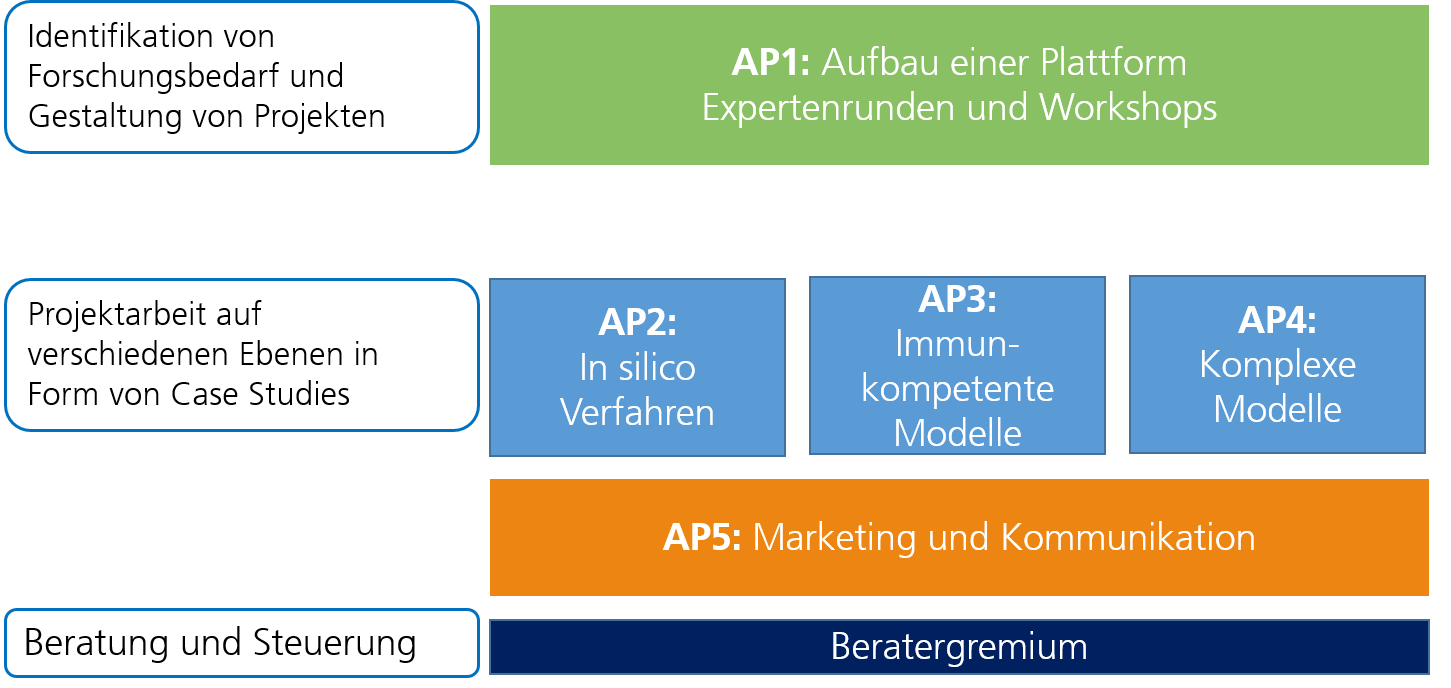
Fraunhofer on the road to predictive models of the future
Animal experiments are permissible “with reasonable justification” to answer scientific questions in basic research and in biomedical research for the diagnosis and treatment of human and animal diseases. They are also required in regulatory toxicology for legally prescribed approvals of products (e.g. chemicals or pharmaceuticals); in each case, it must be examined “whether the intended purpose can be achieved by other methods or procedures”. These other methods or procedures are often referred to as “alternative methods”. In the narrower sense, they include, above all, approaches that replace animal testing. But they also include approaches that reduce or improve animal testing.
Alternative methods as an integral part of research
Alternative methods are an important, integral part of research. However, this does not necessarily lead to the complete replacement of animal testing. Rather, these approaches exist in parallel and/or complement each other. In addition, only a very small proportion of animal testing can (so far) be completely replaced by alternative methods.
There are a variety of methods or procedures to avoid, reduce or mitigate the expected suffering of animals in experiments. These alternative methods or procedures are based, for example, on computer models, cell and tissue cultures, the use of alternative organisms or the refinement of animal testing. Nevertheless, there is an enormous demand for, for example, predictive computer-based models or test systems that predict the complex disease process in the patient.
 Fraunhofer Cluster of Excellence Immune-Mediated Diseases
Fraunhofer Cluster of Excellence Immune-Mediated Diseases