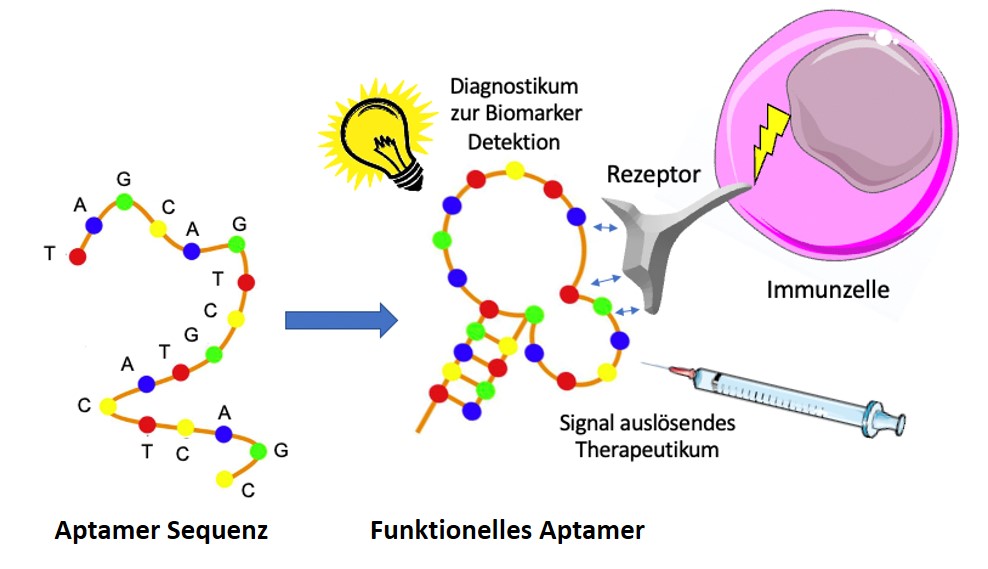
The platform “Aptamers/Tolerogenic Protein Complexes” aims to create cross-institutional structures and networks for research and development of MHCII-glycopeptide complexes for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis (RA) and aptamers for the early detection of glycosylation defects in autoimmune diseases or their precursors.
Treatment options for long-term disease control are needed
For (auto)immune-mediated diseases such as RA, there is a great need for new therapeutic options. With available treatment options such as cytokine blockers, remission or even cure of the disease is rarely achieved. At the same time, these diseases are often diagnosed only after manifestation of irreversible damage. There is therefore a great need for new methods for early diagnosis and for treatment options for the long-term control of the disease-sustaining autoimmunity.
Preliminary work
In extensive preliminary work, a recombinant complex consisting of the MHC II (DRA / DRB1 * 0401) molecule and a galactosylated collagen II peptide has already been developed as an antirheumatic agent and its immunoregulatory potential has been demonstrated in numerous preclinical data. At the same time, methods for glycan isolation and the synthesis of biotinylated glycan structures were established, which can be used for aptamer selection.
Optimization of the formulation and glycosylation of MHC-II complexes
The main objectives of the project are to optimize the formulation and glycosylation of MHC-II glycopeptide complexes, to study them in a humanized mouse model of RA and to identify aptamers for the development of a detection system for glycosylation changes.
 Fraunhofer Cluster of Excellence Immune-Mediated Diseases
Fraunhofer Cluster of Excellence Immune-Mediated Diseases